The historic move by Japan’s central bank this week to scrap negative interest rates and raise them, for the first time in 17 years, is set to transform life, and business, in the island nation.
For the moment, the news is still symbolic because rates remain pinned near zero, yet it has opened the door to something that Japan hasn’t seen in decades – the threat of rising rates.
Now, millions of Japanese, from small business people to first-time homebuyers, are sizing up how to adapt to higher borrowing costs after the long, lean years of deflation, when prices, wages and the cost of money changed little.
ALSO SEE: China Regulator Ramps up Crackdown With Fund Inspections
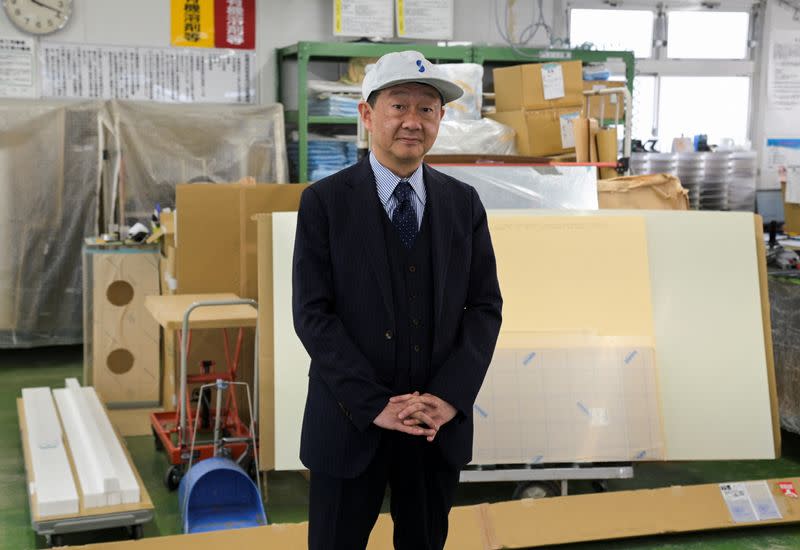
For Satoaki Kanoh, the owner of a small business, he is concerned about costs of a major undertaking becoming more expensive. In coming years, he needs to replace almost a dozen ageing machines at his Tokyo-based maker of acrylic panels.
“Ideally, I’d like to do one a year. But I don’t have that much money,” Kanoh said of the customised pieces of machinery that cost around 50 million yen ($330,000) apiece.
“If we have to pay a lot to borrow, we could end up in a really tough spot.”
He and many other Japanese are now reflecting on the implications for an economy where small and medium-sized companies employ about 70% of the workforce and private consumption accounts for more than half of the gross domestic product.
Kanoh worries about the potential pace of rate increases; too much too quickly and Japan won’t be able to adapt, he said.
His company, Shinshi Co, has about 100 million yen in loans now, but that’s at a fixed rate. Even on a smaller loan of about 10 million yen, the difference between 3% and 1% would be considerable, with the annual interest payment on 3% equivalent to an one employee’s monthly salary, he said.
Battle with the deflationary mindset
Japanese companies and households have long stuck to a deflation playbook: hoard cash and cut costs. That left the economy in a vicious cycle of stop-start growth and flat-lining wages.
Shaking off that deflationary mindset, may prove difficult, even as prices, and some wages, go up.
While big companies are now giving some of the largest pay increases in decades, it’s less clear how much will trickle down to smaller firms.
Around 60% of Japanese firms expect rates to rise to 0.25% by the end of the year, a Reuters survey showed on Thursday. Many said they are looking to front-load spending before borrowing costs rise.
Eiichi Hagiwara, who owns a Tokyo-based designer of water treatment equipment, says higher borrowing costs could eat into the already razor-thin margins at small companies.
For him, that could take bigger projects off the table, as those require loans to cover materials and other costs up front, he said. Having to pay interest ultimately means lower profit margins.
“There’s no work with big margins now,” Hagiwara said. “If I don’t lower prices I can’t get the work.”
Generally he eschews lending, preferring to keep cash reserves for operational costs. He also relies on soft skills, such as taking customers out to cement relationships.
The 76-year-old set up his company, EN-TEC, two decades ago and employs around 20 people. One key to success is being prudent, and ensuring prices are kept low to preserve business ties.
“You have to make sure to take the minimum profit you can,” he said. “If you borrow money and interest rates go up, you’ll be in trouble.”
Hagiwara has only taken out a big loan once, about a decade ago, for around 100 million yen to buy the building for the company headquarters.
But word of the loan soon got out and associates and competitors assumed the company was in trouble. Hagiwara then decided to pay it back in full, which he did within half a year of borrowing the money.
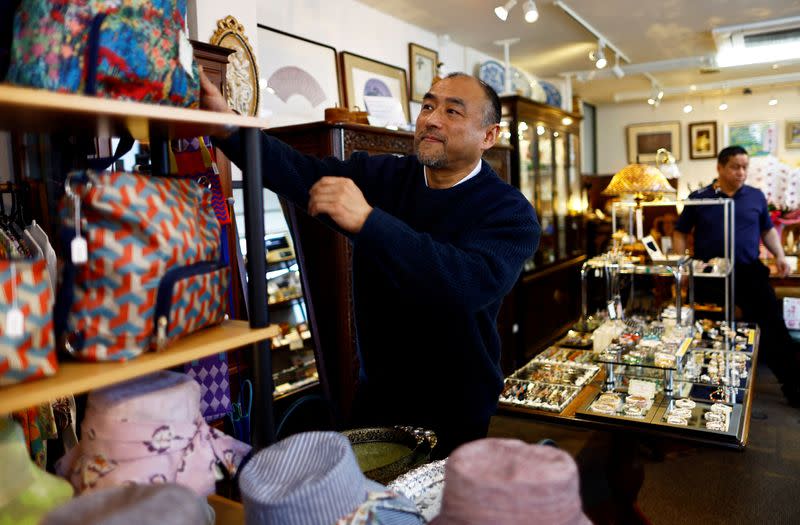

Putting a floor under the weak yen
Some business owners, especially those reliant on imports, hope interest rates could finally put a floor under the weak yen. The currency’s chronic sell-off has driven up the cost of food and fuel.
For Yasunobu Tashiro, who runs a restaurant and a shop selling handbags and other imported goods in the hot spring town of Kinugawa Onsen, the yen has been a massive headache.
“We’re in the import business so the weak yen has been causing us a lot of trouble when we go overseas,” he said. Purchases that used to cost the equivalent of $6,700 now cost $10,000 he said.
However, Haruka Yoda, a 29-year-old IT engineer, is more upbeat. He’s borrowed money to buy a home with his wife and one-month-old baby.
“I feel hopeful that they won’t move too much,” he said. “Even if interest rates rise significantly our salaries might also go up,” he said.
(At the time of publication, the currency was 151 yen to the US dollar).
- Reuters with additional editing by Jim Pollard
ALSO SEE:
BOJ’s Ueda Sure of Inflation’s Momentum, Vows to Back Economy
BOJ Split on When to End Negative Rates, so Ueda Bit the Bullet
Japan Silent on Yen Intervention as Currency’s Slide Continues
Yield Curve Call Sparks BOJ Policy Doubts as Yen Struggles
Japan Admits Spending $48 Billion Rescuing Plummeting Yen
Bank of Japan Chief Ueda Vows to Stick With Easy Policy