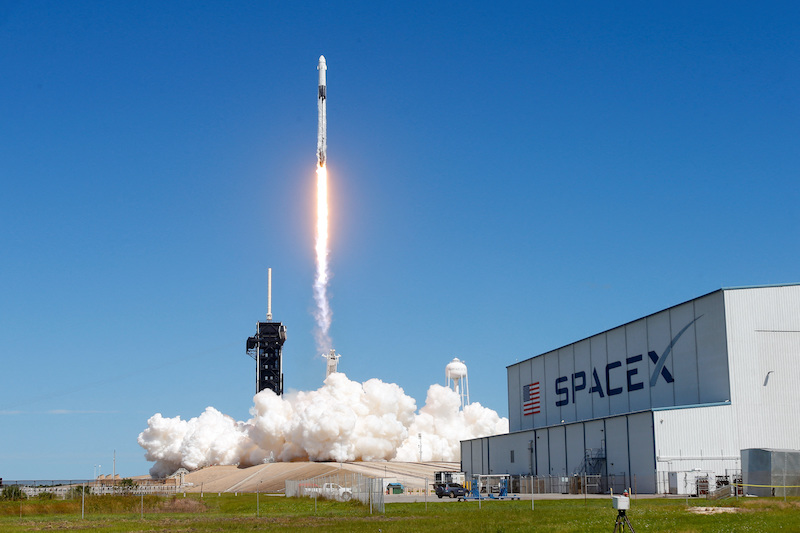
Details have emerged about a vast satellite network that Elon Musk’s SpaceX group is setting up for a US intelligence agency.
SpaceX’s Starshield unit has signed a classified $1.8-billion contract in 2021 with the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) – an intelligence agency that manages ‘spy’ satellites, five sources have told Reuters.
The network, which has or will involve hundreds of low-Earth orbit satellites, reveals the deep ties between the billionaire’s space company and US national security agencies, which became obvious after the start of the war in Ukraine.
ALSO SEE: China’s Surging Exports Tipped to Spur Global Backlash – NYT
The sources said the system, which aims to support ground forces would, if successful, significantly advance the ability of the US government and military to quickly spot potential targets almost anywhere around the globe.
The contract signals growing trust by the intelligence establishment of a company whose owner has clashed with the Biden administration and sparked controversy over the use of Starlink satellite connectivity in the Ukraine war, the sources said.
The Wall Street Journal reported in February the existence of a $1.8-billion classified Starshield contract with an unknown intelligence agency without detailing the purposes of the project.
This report discloses for the first time that the SpaceX contract is for a powerful new spy system with hundreds of satellites bearing Earth-imaging capabilities that can operate as a swarm in low orbits, and that the spy agency that Musk’s company is working with is the NRO.
Reuters was unable to determine when the new network of satellites would come online and could not establish what other companies are part of the programme with their own contracts.
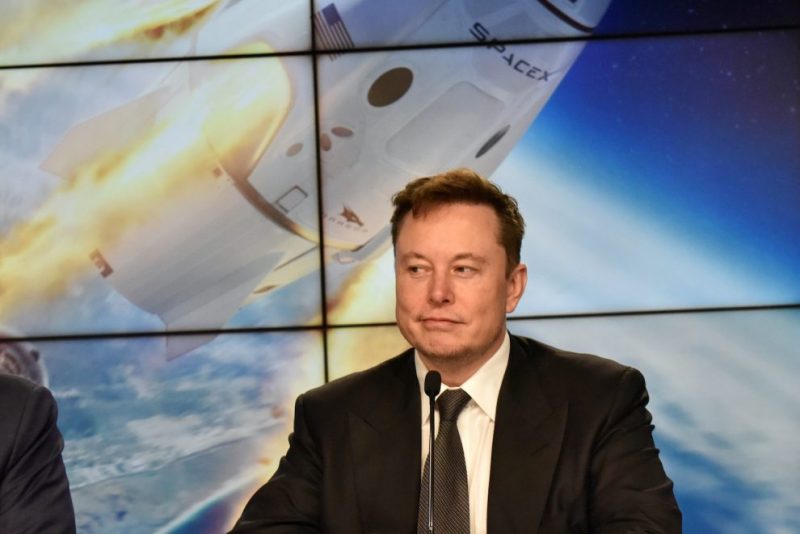

Pentagon a big SpaceX client
SpaceX, the world’s largest satellite operator, did not respond to several requests for comment about the contract, its role in it and details on satellite launches. The Pentagon referred a request for comment to the NRO and SpaceX.
In a statement, the NRO acknowledged its mission to develop a sophisticated satellite system and its partnerships with other government agencies, companies, research institutions and nations, but declined to comment on the extent of SpaceX’s involvement in the effort.
“The National Reconnaissance Office is developing the most capable, diverse, and resilient space-based intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance system the world has ever seen,” a spokesperson said.
The satellites can track targets on the ground and share that data with US intelligence and military officials, the sources said. In principle, that would enable the US government to quickly capture continuous imagery of activities on the ground nearly anywhere on the globe, aiding intelligence and military operations, they added.
Roughly a dozen prototypes have been launched since 2020, among other satellites on SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rockets, three of the sources said.
A US government database of objects in orbit shows several SpaceX missions having deployed satellites that neither the company nor the government have acknowledged. Two sources confirmed those to be prototypes for the Starshield network.
All the sources asked to remain anonymous because they were not authorized to discuss the US government project.
The Pentagon is already a big SpaceX customer, using its Falcon 9 rockets to launch military payloads into space. Starshield’s first prototype satellite, launched in 2020, was part of a separate, roughly $200-million contract that helped position SpaceX for the subsequent $1.8-billion award, one of the sources said.
Separate from Starlink internet service

The planned Starshield network is separate from Starlink, SpaceX’s growing commercial broadband constellation that has about 5,500 satellites in space to provide near-global internet to consumers, companies and government agencies.
The classified constellation of spy satellites represents one of the US government’s most sought-after capabilities in space because it is designed to offer the most persistent, pervasive and rapid coverage of activities on Earth.
“No one can hide,” one of the sources said of the system’s potential capability, when describing the network’s reach.
Musk, also the founder and CEO of Tesla and owner of social media company X (formerly Twitter), has driven innovation in space but has caused frustration among some officials in the Biden administration because of his past control of Starlink in Ukraine, where Kyiv’s military uses it for secure communications in the conflict with Russia.
That authority over Starlink in a war zone by Musk, and not the US military, created tension between him and US officials.
Reports have also detailed how Musk’s manufacturing operations, including at SpaceX, have harmed consumers and workers.
The Starshield network is part of intensifying competition between the US and its rivals to become the dominant military power in space, in part by expanding spy satellite systems away from bulky, expensive spacecraft at higher orbits. Instead a vast, low-orbiting network can provide quicker and near-constant imaging of the Earth.
China is reportedly working to set up its own satellite constellation, and the Pentagon has warned of space weapon threats from Russia, which could be capable of disabling entire satellite networks.
Starshield aims to be more resilient to attacks from sophisticated space powers.
The network is also intended to greatly expand the US government’s remote-sensing capabilities and will consist of large satellites with imaging sensors, as well as a greater number of relay satellites that pass the imaging data and other communications across the network using inter-satellite lasers, two of the sources said.
The NRO includes personnel from the US Space Force and CIA and provides classified satellite imagery for the Pentagon and other intelligence agencies.
The spy satellites will house sensors provided by another company, three of the sources said.
- Reuters with additional editing by Jim Pollard
ALSO SEE:
SpaceX’s Talks With Vietnam Over Starlink Internet Hit a Snag
Congress Wants Musk to Explain Satellite Block in Taiwan – Forbes
SpaceX Launches Satellites Able to Beam Signals to Phones
China Seeking Ways to Take Out or Control Enemy Satellites
Elon Musk’s Starlink to Connect With Planes, Trucks, Ships
China May ‘Need to Destroy’ Musk’s Starlink – SCMP
China Fears US Will Use SpaceX to Bring Calamity to World
US Lauds SpaceX Shutdown of Russian EM Attack – Defense News
Elon Musk’s SpaceX Sets Up an Office in Ukraine – WSJ
Pentagon Eyes SpaceX ‘Quick Reaction Force’ – Intercept